MM_W17; Pivot.. why pivot data; discrete vs continous measures
Well this week I am keeping it simple because of some other commitments. For week 17, I had two pieces of information that I scratched my head about. The first is something that is key as a data analyst.. to pivot your data. Tableau loves data to be nicely organized into rows.
This is the data as delivered from Data World.
As you can see the data has many columns for each of the 'categories' of popcorn. This makes the data difficult to work with as columns in tableau. So, typically we will pivot the data so it is in rows. In the example below, this is the end result we wanted to reach. Each team has a category and score assigned.
To get there all we had to do was
1.go to your data tab
2.select (Control + left mouse click) the rows we wanted to pivot
3.Right Click
4.Pivot Data
wala!
The last thing that I got stuck on was I was doing a dual axis chart and I couldn't get the data to present itself right. I needed to change a measure to a discrete measure and not a continuous measure. Let's define what each it;
Discrete vs continuous; Continuous means "forming an unbroken whole, without interruption"; discrete means "individually separate and distinct." In Tableau, fields can be either continuous or discrete. When you drag a field from the Measures area to Columns or Rows, the values are continuous by default and Tableau creates an axis. Discrete data can take on only integer values whereas continuous data can take on any value. For instance the number of cancer patients treated by a hospital each year is discrete but your weight is continuous. Some data are continuous but measured in a discrete way e.g. your age
this is the data continuous;
and discrete;
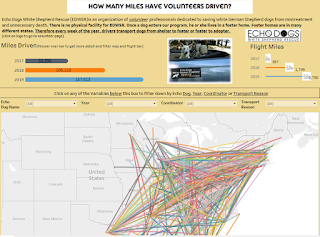
and final link to Viz;





Comments
Post a Comment